 |
| current status |
| mission & introduction |
| goals & objectives |
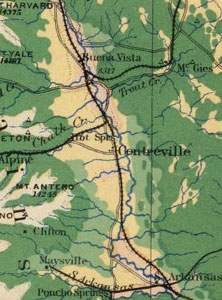
| wildfire hazard maps |
| fire resource list |
| grant opportunities |
| CWPP guidelines |
|
|
Web hosting donated by Colorado Firecamp.
| Community Wildfire Protection Plan | ||||||
| Chaffee County, Colorado | ||||||
| mission and introduction | ||||||
Mission Statement
Introduction
The word “proactive” has twice been banished from the English language for “mis-use, over-use, or general uselessness.” (1991 and 1993, Lake Superior State University.) However, Chaffee County probably merits the word’s return from exile for the measures taken since the early 1990’s to reduce wildfire risk. Considering the county’s fairly minimal history of wildfire occurrence and severity, our efforts have been substantial: subdivision pre-attack wildfire plans, public awareness campaigns including FireWise materials, hazard fuel reduction, slash collection and grinding. We have not waited until after the big fire to reduce fire risk. Regardless, Chaffee County will not receive priority or funding based on a history of “proactive measures.” Recent federal and state legislation, as well as administrative implementation, are requiring a plan. As example, the 2009 Colorado Wildland Urban Interface grant instructions state: “Application must be supported in a Community Wildfire Protection Plan that meets Healthy Forest Restoration Act minimum standards.”
|
||||||